- Veterinary View Box
- Posts
- Accessory Lung Lobe Surgery Safe in Dogs: New Study Confirms Both Left and Right Approaches
Accessory Lung Lobe Surgery Safe in Dogs: New Study Confirms Both Left and Right Approaches
Journal of Small Animal Practice 2025
N. Cremaschini, B. Hertel, A. Singh, A. Aertsens, F. Cinti
Background:
Lobectomy of the accessory lung lobe (ALL) in dogs is rarely reported and considered surgically challenging due to its anatomical position adjacent to critical structures. Previous literature suggested only right-sided thoracotomy was feasible. This study aimed to describe the surgical techniques, complications, and outcomes associated with accessory lung lobectomy via either left- or right-sided intercostal thoracotomy.
Methods:
A retrospective, multicenter case series was conducted reviewing medical records from 11 dogs undergoing ALL lobectomy between 2009 and 2023. Data collected included clinical presentation, imaging findings, surgical approach and technique, intraoperative and postoperative complications, histopathological results, and clinical outcomes. Descriptive statistics summarized findings.
Results:
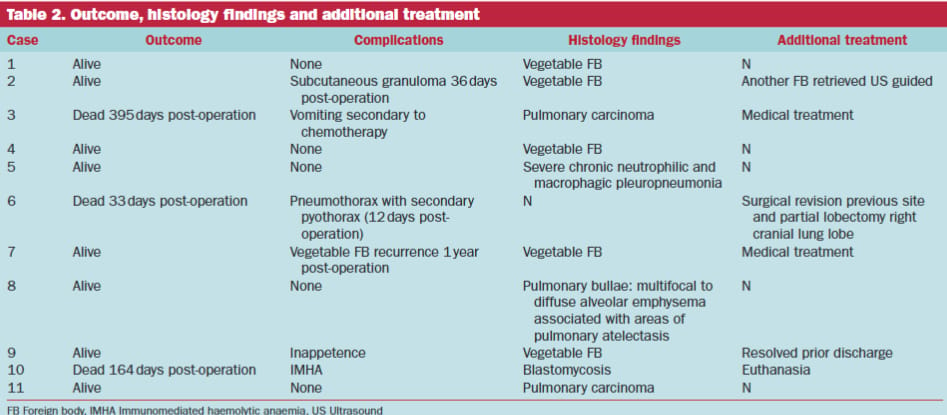
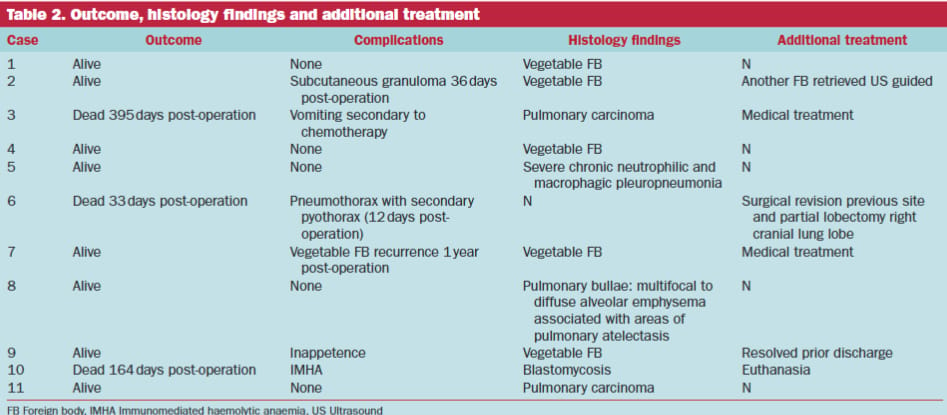
Nine dogs underwent right-sided and two dogs underwent left-sided thoracotomy. Partial lobectomy was performed in six cases and total lobectomy in five cases. Stapler devices were used in 10 dogs. Histopathological diagnoses included pneumonia secondary to foreign body (n=5), pulmonary carcinoma (n=2), chronic neutrophilic and macrophagic pleuropneumonia (n=1), pulmonary bullae (n=1), and blastomycosis (n=1). Minor postoperative complications occurred in five dogs (wound infection, cough, medication reaction, dyspnea, inappetence), while one dog experienced a major complication (pneumothorax requiring revision surgery). All dogs survived to discharge. Median hospitalization time was 15 days. At last follow-up, three dogs had died, but none due to surgical complications.
Limitations:
The study was retrospective with a small sample size and involved only three veterinary centers. Surgical technique and experience varied among surgeons. The left-sided approach was attempted in only two cases, limiting firm conclusions about its routine feasibility. Long-term follow-up was incomplete for some cases.
Conclusions:
Accessory lung lobectomy in dogs is feasible and generally safe when performed via either right- or left-sided intercostal thoracotomy. Right-sided thoracotomy remains standard, but a left-sided approach may be appropriate in cases with concurrent left lung lesions. Outcomes were favorable, and complications were mostly minor and manageable.
How did we do? |
Disclaimer: The summary generated in this email was created by an AI large language model. Therefore errors may occur. Reading the article is the best way to understand the scholarly work. The figure presented here remains the property of the publisher or author and subject to the applicable copyright agreement. It is reproduced here as an educational work. If you have any questions or concerns about the work presented here, reply to this email.